
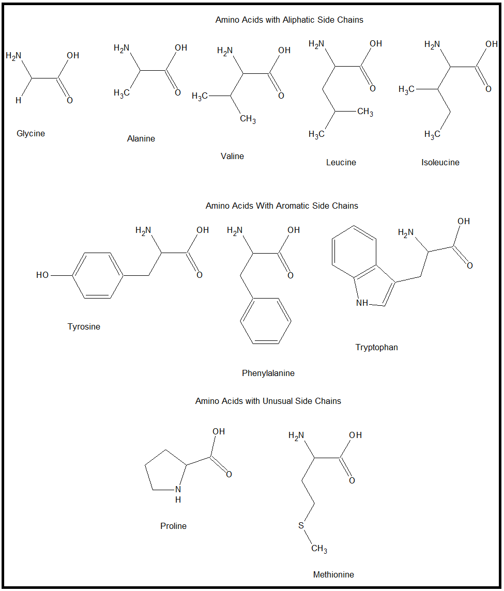
Polar water molecules can form shells around charged or partially charged Water Shells and Polar Surface ResiduesĪcids, mostly found on protein surfaces, promote appropriate folding by interacting Two H-bonds between backbone atoms in leucine 199 and glycine 211 are shown.Ĭ. Most of the model peptide ( residuesġ93-203) is a beta strand that is extensively H-bonded to an adjacent,Īntiparallel beta strand ( residues 206-214). Histidine 40's sidechain provides an - NH donor,Ī backbone carbonyl group ( C= O) group that can accept a hydrogen from a solvent H 2 O at the protein surface.Ī protein are between main chain (backbone) N-H and C= O groups in either alpha helices or beta sheets. Seen here, an H-bond donor ( O) on the sidechain of serine 195 and its corresponding H-bond acceptor ( N) on the sidechain of histidine 57 "share" a partially charged hydrogen.Īn H-bond acceptor (its backbone carbonyl O) and
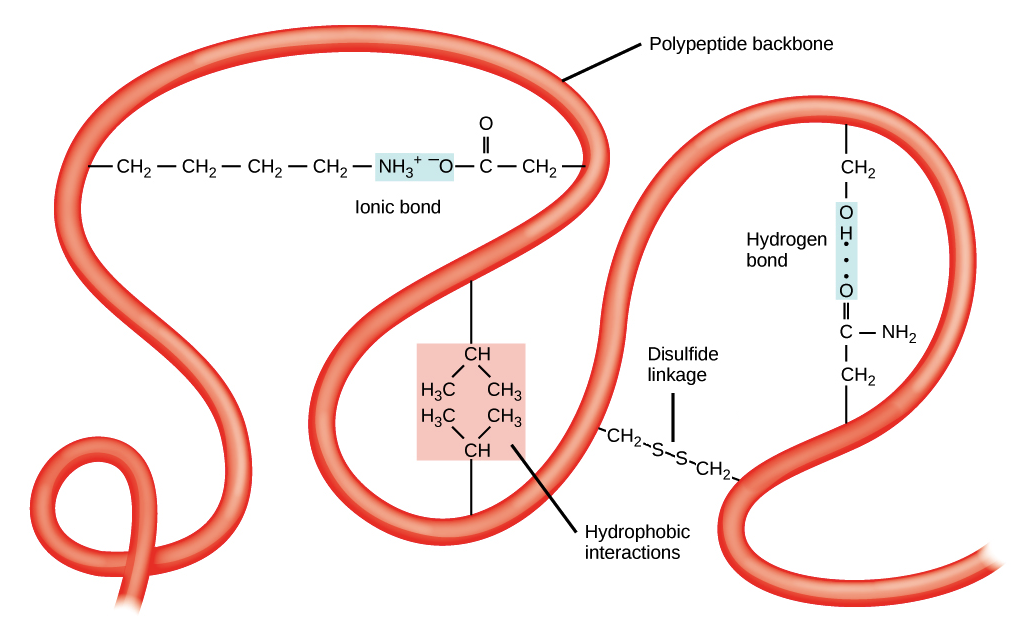
atoms on amino acid sidechains and water molecules at the protein surface.atoms on amino acid sidechains and protein backbone atoms.atoms on two different amino acid sidechains.These can occur between a variety of atoms, involving: The correct 3-D structure of a protein is often dependent on an intricate network of H-bonds. For more background on hydrogen bonds, see the hydrogen bonds page. H-bonds vary in length but are typically in the 1.5-2.5 Å range. Hydrogen, the atoms are engaged in a hydrogen bond (H-bond). Two atoms bearing partial negative charges share a partially positively charged Terminus of chain B ( ile 16), and these atoms engage in an ionic bond (salt bridge). In the model peptide, a negatively charged O on the sidechain of asp 194 lies 2.8 Å from the positively charged N on the amino For more background on ionic bonds, see the ionic bonds page. In the hydrophobic interior of proteins, ionic bonds can even approach the strength of covalent bonds. To protein structure because they are potent electrostatic attractions. Here, cysteine 201 of the model peptide is seen to be covalently bonded with cysteine 136 from an adjacent β-strand.Ītoms of amino acids bearing opposite electrical charges are juxtaposed. The sole amino acid whose side chain can form covalent bonds, yielding disulfideīridges with other cysteine side chains: -CH 2- S - S -CH 2. Side chains can be important determinants of protein structure. For more background on covalent bonds, see the covalentīonds that connect the atoms of a single amino acid and the covalent peptideīond that links amino acids in a protein chain, covalent bonds between cysteine Note that the part of the peptide that spans the interior of the protein comprises multiple amino acids with hydrophobic side chains.īonds are the strongest chemical bonds contributing to protein structure.Ī covalent bond arises when two atoms share a pair of electrons. As will be seen, most residues of this peptide are contained in a β-strand. Backbone atoms are pink and sidechain atoms are in the CPK color scheme: C, H, N, O, P, S (hydrogens not shown). The protein will be used used to illustrate exampleīonds in a known structure. Peptide of 12 amino acids (gly 193-asn 204) of chain C that spans It consists ofįour peptide chains ( A, , B, , C, , D), generated by cleavage of a precursor peptide. The gamma chymotrypsin protein, shown at left, will serve as an example protein. For more background on bonds, including strong and weak bonds, see the chemical bonds page. Shows a few examples of the types of chemical bonds that play important roles in determining and stabilizing 3-D protein structure. To turn off stereo mode, return here and use this button. To turn on stereo mode when viewing a scene, return here and use this button In this mode, when you train one eye on one image and the other eye on the other image, you will elicit a centered image that appears truly 3-dimensional. If you are a practiced user, you can create the illusion of 3D if you turn on stereo mode. To evoke renderings of the molecule that illustrate particular In Chrome, you can click on the popup blocker icon in the right part of the address bar.

If using a browser other than Firefox (the recommended browser for this site), be sure to allow popups. Use the scroll bar to scroll through the text. This exhibit displays molecules in the left part of the screen, and text that addresses structure-function relationships in the right pane. Please leave comments/suggestions or please acknowledge use of this site by visiting our feedback page An Introduction to Chemical Bonds and Protein Structure


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
